All about SGST, CGST, IGST and UTGST
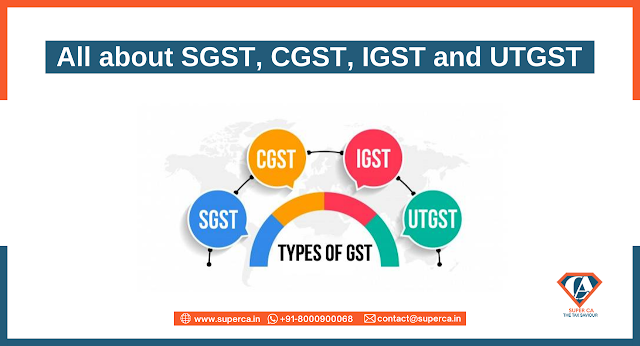
Implementation of GST in India was a big move, as it marked a significant indirect tax reform in the country. The amalgamation of a large number of taxes which was levied at a central and state level into a single tax had expected to have big advantages. Almost about four years ago, GST had replaced 17 local levies like excise duty, service tax, VAT and 13 cesses. Most of the complex indirect system problems have also been eased by GST with a simple, transparent and technology-driven tax regime and has thus integrated India into a single common market. Further, Tax arbitrage across states that distorted business investment decisions has also been eliminated by the implementation of GST. In this article, we’ll talk about the different types of GST namely SGST, CGST, UTGST and IGST, their structure and a basic difference between them. Types of GST and its Explanation As per the newly implemented GST regime, there are 4 different types of GST namely : Integrated Goods and Services...